Git - Version Control

Git is an open-source distributed version control system designed to track changes in files and coordinate work on those files among multiple people and locations. It is primarily used to allow programmers to work together in a codebase.
One might never know all the git commands because they are numerous but there are some that every developer is expected to know to be able to collaborate with other developers.
Branch
Branching allows each developer to branch out from the original code base and isolate their work from others. It also helps Git to easily merge versions later on.
Imagine that you are working with your colleagues on the same file. There is a solid chance that someone will, at least partially, overwrite one other’s work. We can avoid that by branching in order to isolates our work from that of other team members.
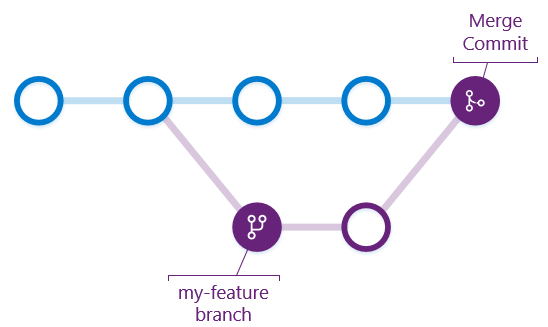
In short, a Git branch is an independent line of development. Note: each node on the image above represents a commit.
$ git checkout -b [branch name] // Create a new branch and switch to it
Commit
To commit is the action of adding your changes to the local repository. It needs to be accompanied with a commit message that describes what this change is bringing to the code base:
$ git commit -m "This fix a bug in the code base" // Commit changes
We recommend to use a GUI to manage commits, it gives us a better view on what we want to commit.$ git gui // (git-gui)
Conflicts
When working in Git, users can combine commits from two different branches through an action known as merging. Files are automatically merged unless the commits update the same line of code differently. In that case there is a conflict: which version of this line should be taken?
Merge conflicts can traditionally cause developers a lot of grief when working in the terminal. This is why we advise to use a GUI (such as meld) to resolve conflicts.
Github
GitHub, Inc. is a US-based global company that provides hosting for software development version control using Git. This is the world's largest open source platform. It is now a subsidiary of Microsoft, which acquired the company in 2018 for US$7.5 billion.

Merge
To merge one branch into another is the action of fusing 2 different versions of the project together. If you are done working on a branch named “my-feature”, you can merge it to master in order for the master branch to be updated with your work.
$ git merge [source branch] [target branch] // Merge a branch into a target branch

Pull
This is the action of updating your local version of a repository to the newest commit. Do not forget to do it before starting to work on something!
$ git pull // Update local repository to the newest commit
Push
This is the action of sending your commits to the remote repository (on GitHub or GitLab, for example).
$ git push // Push changes to remote repository
Repository (repo)
Take it as a folder that contains all the source files and tracks all the changes made, building a history over time. On Github, each project is a repo.
